Its massive investment in education has taken the country from mass illiteracy to a major international technological powerhouse. The country’s national economy benefits from a highly skilled workforce and is among the most educated countries in the world with one of the highest percentages of its citizens holding a tertiary education degree. South Korea’s economy was one of the world’s fastest-growing from the early 1960s to the late 1990s, and was still one of the fastest-growing developed countries in the 2000s, along with Hong Kong, Singapore and Taiwan, the other three Asian Tigers. It recorded the fastest rise in average GDP per capita in the world between 1980 and 1990. South Koreans refer to this growth as the Miracle on the Han River. The South Korean economy is heavily dependent on international trade, and in 2014, South Korea was the fifth-largest exporter and seventh-largest importer in the world.
Despite the South Korean economy’s high growth potential and apparent structural stability, the country suffers damage to its credit rating in the stock market because of the belligerence of North Korea in times of deep military crises, which has an adverse effect on South Korean financial markets. The International Monetary Fund compliments the resilience of the South Korean economy against various economic crises, citing low state debt and high fiscal reserves that can quickly be mobilized to address financial emergencies. Although it was severely harmed by the Asian economic crisis of the late 1990s, the South Korean economy managed a rapid recovery and subsequently tripled its GDP.
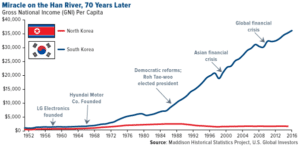
Furthermore, South Korea was one of the few developed countries that were able to avoid a recession during the global financial crisis. Its economic growth rate reached 6.2 percent in 2010 (the fastest growth for eight years after significant growth by 7.2 percent in 2002), a sharp recovery from economic growth rates of 2.3% in 2008 and 0.2% in 2009, when the global financial crisis hit. The unemployment rate in South Korea also remained low in 2009, at 3.6%.
South Korea became a member of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) in 1996.
Transportation:
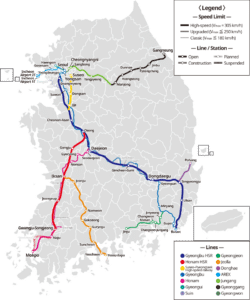
South Korea has a technologically advanced transport network consisting of high-speed railways, highways, bus routes, ferry services, and air routes that crisscross the country. Korea Expressway Corporation operates the toll highways and service amenities en route.
Korail provides frequent train services to all major South Korean cities. Two rail lines, Gyeongui and Donghae Bukbu Line, to North Korea are now being reconnected. The Korean high-speed rail system, KTX, provides high-speed service along Gyeongbu and Honam Line. Major cities including Seoul, Busan, Incheon, Daegu, Daejeon and Gwangju have urban rapid transit systems. Express bus terminals are available in most cities.
South Korea’s main gateway and largest airport is Incheon International Airport, serving 58 million passengers in 2016. Other international airports include Gimpo, Busan and Jeju. There are also many airports that were built as part of the infrastructure boom but are barely used. There are also many heliports.
