On 6 February 2019, the permanent representatives of NATO member states and Macedonian Foreign Affairs Minister Nikola Dimitrov, signed in Brussels the accession protocol of North Macedonia into NATO. The protocol was then ratified on 8 February by the Greek parliament, thus completing all the preconditions for putting into force the Prespa agreement. Subsequently, on 12 February the Macedonian government announced the formal activation of the constitutional amendments which effectively renamed the country as North Macedonia and informed accordingly the United Nations and its member states.
In March 2020, after the ratification process by all NATO members was completed, North Macedonia acceded to NATO, becoming the 30th member state.

The same month, the leaders of the European Union formally gave approval to North Macedonia begin talks to join the EU.
Geography:
North Macedonia has a total area of 25,713 km2 (9,928 sq mi). North Macedonia has some 748 km (465 mi) of boundaries, shared with Serbia (62 km or 39 mi) to the North, Kosovo (159 km or 99 mi) to the northwest, Bulgaria (148 km or 92 mi) to the east, Greece (228 km or 142 mi) to the south, and Albania (151 km or 94 mi) to the west.
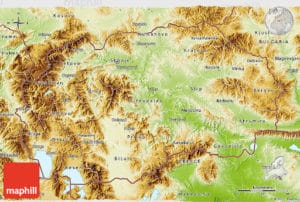
North Macedonia is a landlocked country that is geographically clearly defined by a central valley formed by the Vardar river and framed along its borders by mountain ranges. The terrain is mostly rugged, located between the Šar Mountains and Osogovo, which frame the valley of the Vardar river. Three large lakes—Lake Ohrid, Lake Prespa and Dojran Lake—lie on the southern borders, bisected by the frontiers with Albania and Greece. Ohrid is considered to be one of the oldest lakes and biotopes in the world. The region is seismically active and has been the site of destructive earthquakes in the past, most recently in 1963 when Skopje was heavily damaged by a major earthquake, killing over 1,000.
North Macedonia also has scenic mountains. They belong to two different mountain ranges: the first is the Šar Mountains that continues to the West Vardar/Pelagonia group of mountains (Baba Mountain, Nidže, Kozuf and Jakupica), also known as the Dinaric range. The second range is the Osogovo–Belasica mountain chain, also known as the Rhodope range. The mountains belonging to the Šar Mountains and the West Vardar/Pelagonia range are younger and higher than the older mountains of the Osogovo-Belasica mountain group. Mount Korab of the Šar Mountains on the Albanian border, at 2,764 m (9,068 ft), is the tallest mountain in North Macedonia. In North Macedonia there are 1,100 large sources of water. The rivers flow into three different basins: the Aegean, the Adriatic and the Black Sea.

The Aegean basin is the largest. It covers 87% of the territory of North Macedonia, which is 22,075 square kilometers (8,523 sq mi). Vardar, the largest river in this basin, drains 80% of the territory or 20,459 square kilometers (7,899 sq mi). Its valley plays an important part in the economy and the communication system of the country. The Vardar Valley project is considered to be crucial for the strategic development of the country. The river Black Drin forms the Adriatic basin, which covers an area of about 3,320 km2 (1,282 sq mi), i.e., 13% of the territory. It receives water from Lakes Prespa and Ohrid. The Black Sea basin is the smallest with only 37 km2 (14 sq mi). It covers the northern side of Mount Skopska Crna Gora. This is the source of the river Binachka Morava, which joins the Morava, and later, the Danube, which flows into the Black Sea. North Macedonia has around fifty ponds and three natural lakes, Lake Ohrid, Lake Prespa and Lake Dojran. In North Macedonia there are nine spa towns and resorts: Banište, Banja Bansko, Istibanja, Katlanovo, Kežovica, Kosovrasti, Banja Kočani, Kumanovski Banji and Negorci.
Economy:
Ranked as the fourth “best reformatory state” out of 178 countries ranked by the World Bank in 2009, North Macedonia has undergone considerable economic reform since independence. The country has developed an open economy with trade accounting for more than 90% of GDP in recent years. Since 1996, North Macedonia has witnessed steady, though slow, economic growth with GDP growing by 3.1% in 2005. This figure was projected to rise to an average of 5.2% in the 2006–2010 period.
