The first oil was discovered at the small Balder field in 1967, production only began in 1999. In 1969, the Phillips Petroleum Company discovered petroleum resources at the Ekofisk field west of Norway. In 1973, the Norwegian government founded the State oil company, Statoil. Oil production did not provide net income until the early 1980s because of the large capital investment that was required to establish the country’s petroleum industry.

Around 1975, both the proportion and absolute number of workers in industry peaked. Since then labor-intensive industries and services like factory mass production and shipping have largely been outsourced.
Norway was a founding member of the European Free Trade Association (EFTA). Norway was twice invited to join the European Union, but ultimately declined to join after referendums that failed by narrow margins in 1972 and 1994.

In 2011, Norway suffered two terrorist attacks on the same day conducted by Anders Behring Breivik which struck the government quarter in Oslo and a summer camp of the Labour party’s youth movement at Utøya island, resulting in 77 deaths and 319 wounded.
Geography:
Norway’s core territory comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula; the remote island of Jan Mayen and the archipelago of Svalbard are also part of the Kingdom of Norway. The Antarctic Peter I Island and the sub-Antarctic Bouvet Island are dependent territories and thus not considered part of the Kingdom. Norway also lays claim to a section of Antarctica known as Queen Maud Land.
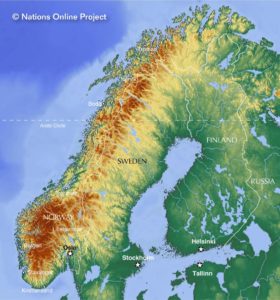
The rugged coastline is broken by huge fjords and thousands of islands. The coastal baseline is 2,532 kilometers (1,573 mi). The coastline of the mainland including fjords stretches 28,953 kilometers (17,991 mi), when islands are included the coastline has been estimated to 100,915 kilometers (62,706 mi). Norway shares a 1,619-kilometre (1,006 mi) land border with Sweden, 727 kilometers (452 mi) with Finland, and 196 kilometers (122 mi) with Russia to the east. To the north, west and south, Norway is bordered by the Barents Sea, the Norwegian Sea, the North Sea, and Skagerrak. The Scandinavian Mountains form much of the border with Sweden.
The land is mostly made of hard granite and gneiss rock, but slate, sandstone, and limestone are also common, and the lowest elevations contain marine deposits.
Economy:
Norwegians enjoy the second-highest GDP per-capita among European countries (after Luxembourg), and the sixth-highest GDP (PPP) per-capita in the world. Today, Norway ranks as the second-wealthiest country in the world in monetary value, with the largest capital reserve per capita of any nation. Norway maintained first place in the world in the UNDP Human Development Index (HDI) for six consecutive years (2001–2006), and then reclaimed this position in 2009. The standard of living in Norway is among the highest in the world. Foreign Policy magazine ranks Norway last in its Failed States Index for 2009, judging Norway to be the world’s most well-functioning and stable country. The OECD ranks Norway fourth in the 2013 equalised Better Life Index and third in intergenerational earnings elasticity.
