Poland joined the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) alliance in 1999 along with the Czech Republic and Hungary. Poles then voted to join the European Union in a referendum in June 2003, with Poland becoming a full member on 1 May 2004. Poland joined the Schengen Area in 2007.
On 10 April 2010, the President of the Republic of Poland, Lech Kaczyński, along with 89 other high-ranking Polish officials died in a plane crash near Smolensk, Russia. The president’s party was on their way to attend an annual service of commemoration for the victims of the Katyń massacre when the tragedy took place.

The 2015 and 2019 elections were won by the conservative Law and Justice Party (PiS), resulting in increased friction between Poland and the EU. In December 2017, Mateusz Morawiecki was sworn in as the new Prime Minister, succeeding Beata Szydlo, in office since 2015. They both represented ruling Law and Justice party, led by powerful Jaroslaw Kaczynski. President Andrzej Duda, supported by Law and Justice party, was narrowly re-elected in the 2020 presidential election.
Geography:
Poland’s vast territory covers approximately 312,696 km2 (120,733 sq mi), of which 98.52% is dry land and 1.48% is water. Extending across several geographical regions, the country is the 9th-largest by area in Europe and 69th largest in the world. Topographically, Poland is diverse and has access to the sea, the mountains and open terrain. Although most of the central parts of the country are flat, there is an abundance of lakes, rivers, hills, swamps, beaches, islands and forests elsewhere.
In the north-west is the Baltic seacoast spanning from the Bay of Pomerania to the Gulf of Gdańsk. The coast is marked by several spits, coastal lakes (former bays that have been cut off from the sea), and dunes. The largely straight coastline is indented by the Szczecin Lagoon, the Bay of Puck, and the Vistula Lagoon.
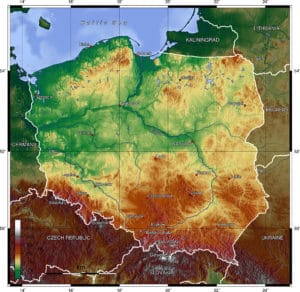
The central and northern parts of the country lie within the North European Plain. Rising above these lowlands is a geographical region comprising four hilly districts of moraines and moraine-dammed lakes formed during and after the Pleistocene ice age, notably the Pomeranian Lake District, the Greater Polish Lake District, the Kashubian Lake District, and the Masurian Lake District. The Masurian Lake District is the largest of the four and covers much of north-eastern Poland.
South of the Northern European Plain are the regions of Lusatia, Silesia and Masovia, which are marked by broad ice-age river valleys. The extreme south of Poland is mountainous; it runs from the Sudetes in the west to the and the Carpathian Mountains in the east. The highest part of the Carpathian massif is the Tatra Mountain range, along Poland’s southern border.
Economy:
Poland’s economy and Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is currently the sixth largest in the European Union by nominal standards, and the fifth largest by purchasing power parity. It is also one of the fastest growing within the Union. Around 60% of the employed population belongs to the tertiary service sector, 30% to industry and manufacturing, and the remaining 10% to the agricultural sector. Although Poland is a member of EU’s single market, the country has not adopted the Euro as legal tender and maintains its own currency – the Polish złoty (zł, PLN).
