Russia has one of the world’s largest surface water resources; with its lakes containing approximately one-quarter of the world’s liquid fresh water. The largest and most prominent of Russia’s bodies of fresh water is Lake Baikal, the world’s deepest, purest, oldest and most capacious fresh water lake; which alone contains over one-fifth of the world’s fresh surface water. Other major lakes include Ladoga and Onega, two of the largest lakes in Europe. Russia is second only to Brazil in volume of the total renewable water resources. Out of the country’s 100,000 rivers, the Volga is the most famous—it is the longest river in Europe. The Siberian rivers of Ob, Yenisey, Lena and Amur are among the world’s longest rivers.
Economy:
Russia has an upper-middle income mixed and transition economy, with enormous natural resources, particularly oil and natural gas. It has the world’s eleventh-largest economy by nominal GDP and the sixth-largest by PPP. According to the IMF, Russia’s GDP per capita by PPP is $29,485 as of 2021. Approximately 12.9% of Russians lived below the national poverty line in 2018. Unemployment in Russia was 4.5% in 2019, and officially more than 70% of the Russian population is categorized as middle class; though this is disputed. By the end of December 2019, Russian foreign trade turnover reached $666.6 billion. Russia’s exports totaled over $422.8 billion, while its imported goods were worth over $243.8 billion.
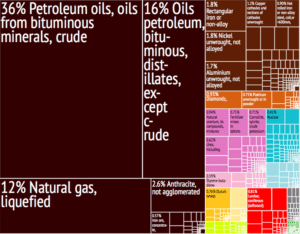
Oil, natural gas, metals, and timber account for more than 80% of Russian exports abroad. In 2016, the oil-and-gas sector accounted for 36% of federal budget revenues. In 2019, the Natural Resources and Environment Ministry estimated the value of natural resources to 60% of the country’s GDP. Russia has one of the lowest foreign debts among major economies. It ranked 28th of 190 countries in the 2019 Ease of Doing Business Index. Russia has a flat tax rate of 13%; with the world’s second-most attractive personal tax system for single managers after the United Arab Emirates. However, extreme inequality of household income and wealth in the country has also been noted.
Transportation:
Railway transport in Russia is mostly under the control of the state-run Russian Railways. The total length of common-used railway tracks exceeds 85,500 km (53,127 mi), second only to the United States. The most renowned railway in Russia is the Trans-Siberian Railway, the longest railway-line in the world.

As of 2016, Russia had 1,452.2 km of roads, and its road density is the lowest among the BRICS.
Among Russia’s 1,216 airports, the busiest are Sheremetyevo, Domodedovo, and Vnukovo in Moscow, and Pulkovo in Saint Petersburg.

Major seaports of Russia include Rostov-on-Don on the Sea of Azov, Novorossiysk on the Black Sea, Astrakhan and Makhachkala on the Caspian Sea, Kaliningrad and Saint Petersburg on the Baltic Sea, Arkhangelsk on the White Sea, Murmansk on the Barents Sea, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky and Vladivostok on the Pacific Ocean. The world’s only fleet of nuclear-powered icebreakers advances the economic exploitation of the Arctic continental shelf of Russia and the development of sea trade through the Northern Sea Route.
Flag of Russia:
The flag of the Russian Federation is a tricolor flag consisting of three equal horizontal fields: white on the top, blue in the middle, and red on the bottom. The flag was first used as an ensign for Russian merchant ships in 1696.
