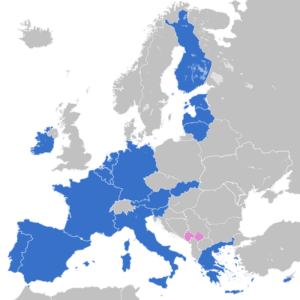
The European Union Nations are:
- Austria
- Belgium
- Bulgaria
- Croatia
- Cyprus
- Czech Republic
- Denmark
- Estonia
- Finland
- France
- Germany
- Greece
- Hungary
- Ireland
- Italy
- Latvia
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Malta
- Netherlands
- Poland
- Portugal
- Romania
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Spain
- Sweden
- United Kingdom
The EU’s member states cover an area of 4,423,147 square kilometres. The EU’s highest peak is Mont Blanc in the Graian Alps, 4,810.45 meters above sea level. The lowest points in the EU are Lammefjorden, Denmark and Zuidplaspolder, Netherlands, at 7 m below sea level. The landscape, climate, and economy of the EU are influenced by its coastline, which is 65,993 kilometers long.
Including the overseas territories of France which are located outside the continent of Europe, but which are members of the union, the EU experiences most types of climate from Arctic (North-East Europe) to tropical (French Guiana), rendering meteorological averages for the EU as a whole meaningless. The majority of the population lives in areas with a temperate maritime climate (North-Western Europe and Central Europe), a Mediterranean climate (Southern Europe), or a warm summer continental or hemiboreal climate (Northern Balkans and Central Europe).
The EU’s population is highly urbanised, with some 75% of inhabitants living in urban areas as of 2006. Cities are largely spread out across the EU, although with a large grouping in and around the Benelux.
Economy:
The European Union has established a single market across the territory of all its members representing 512 million citizens. In 2017, the EU had a combined GDP of $21 trillion international dollars, a 17% share of global gross domestic product by purchasing power parity (PPP). As a political entity the European Union is represented in the World Trade Organization (WTO). EU member states own the estimated second largest after the United States (US$98.2 trillion) net wealth in the world, equal to 25% (US$78 trillion) of the $317 trillion(~€280 trillion) global wealth.
19 member states have joined a monetary union known as the eurozone, which uses the Euro as a single currency. The currency union represents 342 million EU citizens. The euro is the second largest reserve currency as well as the second most traded currency in the world after the United States dollar.
Of the top 500 largest corporations in the world measured by revenue in 2010, 161 have their headquarters in the EU. In 2016, unemployment in the EU stood at 8.9% while inflation was at 2.2%, and the current account balance at −0.9% of GDP. The average annual net earnings in the European Union was around €24,000 (US$30,000) in 2015, which was about 70% of that in the United States.
Structural Funds and Cohesion Funds are supporting the development of underdeveloped regions of the EU. Such regions are primarily located in the states of central and southern Europe. Several funds provide emergency aid, support for candidate members to transform their country to conform to the EU’s standard (Phare, ISPA, and SAPARD), and support to the Commonwealth of Independent States (TACIS). TACIS has now become part of the worldwide EuropeAid programme. EU research and technological framework programmes sponsor research conducted by consortia from all EU members to work towards a single European Research Area.
Internal Market:
Two of the original core objectives of the European Economic Community were the development of a common market, subsequently becoming a single market, and a customs union between its member states. The single market involves the free circulation of goods, capital, people, and services within the EU, and the customs union involves the application of a common external tariff on all goods entering the market. Once goods have been admitted into the market they cannot be subjected to customs duties, discriminatory taxes or import quotas, as they travel internally. The non-EU member states of Iceland, Norway, Liechtenstein and Switzerland participate in the single market but not in the customs union. Half the trade in the EU is covered by legislation harmonised by the EU.
