Meanwhile, Andreas Papandreou, George Papandreou’s son, founded the Panhellenic Socialist Movement (PASOK) in response to Karamanlis’s conservative New Democracy party, with the two political formations dominating in government over the next four decades. Greece rejoined NATO in 1980. Greece became the tenth member of the European Communities (subsequently subsumed by the European Union) on 1 January 1981, ushering in a period of sustained growth. Widespread investments in industrial enterprises and heavy infrastructure, as well as funds from the European Union and growing revenues from tourism, shipping, and a fast-growing service sector raised the country’s standard of living to unprecedented levels. Traditionally strained relations with neighbouring Turkey improved when successive earthquakes hit both nations in 1999, leading to the lifting of the Greek veto against Turkey’s bid for EU membership.
The country adopted the euro in 2001 and successfully hosted the 2004 Summer Olympic Games in Athens. More recently, Greece has suffered greatly from the late-2000s recession and has been central to the related European sovereign debt crisis. Due to the adoption of the euro, when Greece experienced financial crisis, it could no longer devalue its currency to regain competitiveness. Youth unemployment was especially high during the 2000s. The Greek government-debt crisis, and subsequent austerity policies, have resulted in protests and social strife.
Geography:
Located in Southern and Southeast Europe, Greece consists of a mountainous, peninsular mainland jutting out into the sea at the southern end of the Balkans, ending at the Peloponnese peninsula (separated from the mainland by the canal of the Isthmus of Corinth) and strategically located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Due to its highly indented coastline and numerous islands, Greece has the 11th longest coastline in the world with 13,676 km (8,498 mi); its land boundary is 1,160 km (721 mi).
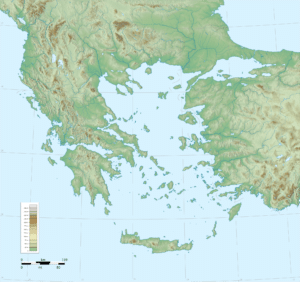
Eighty percent of Greece consists of mountains or hills, making the country one of the most mountainous in Europe. Mount Olympus, the mythical abode of the Greek Gods, culminates at Mytikas peak 2,918 metres (9,573 ft), the highest in the country. Western Greece contains a number of lakes and wetlands and is dominated by the Pindus mountain range. The Pindus, a continuation of the Dinaric Alps, reaches a maximum elevation of 2,637 m (8,652 ft) at Mt. Smolikas (the second-highest in Greece) and historically has been a significant barrier to east–west travel.
The Pindus range continues through the central Peloponnese, crosses the islands of Kythera and Antikythera and finds its way into southwestern Aegean, in the island of Crete where it eventually ends. The islands of the Aegean are peaks of underwater mountains that once constituted an extension of the mainland. Pindus is characterised by its high, steep peaks, often dissected by numerous canyons and a variety of other karstic landscapes. The spectacular Vikos Gorge, part of the Vikos-Aoos National Park in the Pindus range, is listed by the Guinness book of World Records as the deepest gorge in the world. Another notable formation are the Meteora rock pillars, atop which have been built medieval Greek Orthodox monasteries.
