

Isle of Man
In 1250 the Germanic Frederick II, Holy Roman Emperor, died after having ruled Sicily for 52 years. He was King of Sicily from 1198, King of Germany from 1212, King of Italy and Holy Roman Emperor from 1220 and King of Jerusalem from 1225. His mother Constance was Queen of Sicily and his father was Henry VI of the House of Hohenstaufen. Although there is no evidence that the triskeles was used in Sicily in the 13th century, there is architectural evidence of its use in Austria at that time, almost certainly relating to a personal emblem of Frederick, and almost certainly stemming from his Sicilian connection.
Four years after Frederick’s death the pope invested the Sicilian kingship in Edmund Crouchback (died 1296), the second surviving son of Henry III, King of England (died 1272), and for about ten years afterwards Edmund was styled “King of Sicily“. Henry invested considerable political capital in his son’s new position, and in his efforts to raise funds from taxation to support the dignity of that kingship made himself extremely unpopular with his English nobles, who eventually rebelled.
The wife of Alexander III, King of Scotland, was Margaret of England (died 1275), a daughter of King Henry III. This familial connection between the English and Scottish royal families might account for the introduction of the triskeles as a symbol of the Isle of Man. If so, it may well have been adopted as a means to reinforce the regime change on the island.
Following English domination of the isle in 1346, the triskelion was retained and endured as a symbol of the Isle of Man.
By the mid-19th century the Manx flag began appearing on merchant ships from the Isle of Man. However, such usage of the flag was not sanctioned by the Board of Trade and the Admiralty under Section 105 of the 1854 Merchant Shipping Act in favor of the Red Ensign. This decision was reversed by the Admiralty on 4 March 1889 and Manx merchant ships were permitted to fly the Flag of the Isle of Man.
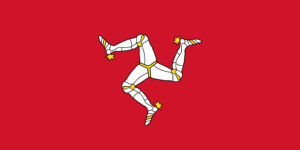
The flag was officially adopted between 1928 and 1932, however sources differ.
In July 1968 steps were taken to standardize the flag. The feet of the triskelion were all to be facing in a clockwise direction and was to be balanced with one leg directly facing to the bottom. On 27 August 1971 a civil ensign for the Isle of Man was approved by royal proclamation. This flag featured a red field with the Union Jack in the canton. The triskelion of Mann is emblazoned off center towards the fly. Another Manx flag in use is the flag of Tynwald, the legislature of the Isle of Man, which has flown outside the Legislative Buildings since 1971.