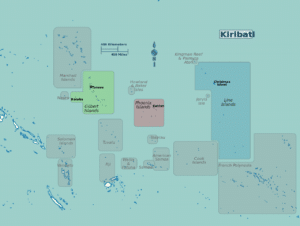
The groups of islands are:
Banaba: an isolated island between Nauru and the Gilbert Islands
Gilbert Islands: 16 atolls located some 1,500 kilometres (932 mi) north of Fiji
Phoenix Islands: 8 atolls and coral islands located some 1,800 kilometres (1,118 mi) southeast of the Gilberts
Line Islands: 8 atolls and one reef, located about 3,300 kilometres (2,051 mi) east of the Gilberts
Banaba (or Ocean Island) is a raised-coral island. It was once a rich source of phosphates, but was exhausted in mining before independence. The rest of the land in Kiribati consists of the sand and reef rock islets of atolls or coral islands, which rise only one or two metres above sea level.

The soil is thin and calcareous. It has a low water-holding capacity and low organic matter and nutrient content—except for calcium, sodium, and magnesium. Banaba is one of the least suitable places for agriculture in the world.
Kiritimati (Christmas Island) in the Line Islands is the world’s largest atoll. Based on a 1995 realignment of the International Date Line, the Line Islands were the first area to enter into a new year, including year 2000. For that reason, Caroline Island has been renamed Millennium Island. The majority of Kiribati, including the capital, is not first, for example New Zealand (UTC+13 in January) has an earlier new year.
Economy:
Kiribati has few natural resources. Commercially viable phosphate deposits on Banaba were exhausted at the time of independence. Copra and fish now represent the bulk of production and exports. Kiribati is considered one of the least developed countries in the world.

In one form or another, Kiribati gets a large portion of its income from abroad. Examples include fishing licences, development assistance, workers’ remittances, especially the seafarers issued from Marine Training Centre, and a few tourists. Given Kiribati’s limited domestic production ability, it must import nearly all of its essential foodstuffs and manufactured items; it depends on these external sources of income for financing.
The economy of Kiribati benefits from international development assistance programs. The multilateral donors providing development assistance in 2009 were the European Union (A$9 million), the United Nations Development Programme (A$3.7 million), UNICEF, and the World Health Organization (A$100,000). The bilateral donors providing development assistance in 2009 were Australia (A$11 million), Japan (A$2 million), New Zealand (A$6.6 million), Taiwan (A$10.6 million), and other donors providing A$16.2 million, including technical assistance grants from the Asian Development Bank.
In 1956, Gilbert and Ellice Islands established a sovereign wealth fund to act as a store of wealth for the country’s earnings from phosphate mining. In 2008, the Revenue Equalization Reserve Fund was valued at US$400 million. The RERF assets declined from A$637 million (420% of GDP) in 2007 to A$570.5 million (350% of GDP) in 2009 as the result of the global financial crisis and exposure to failed Icelandic banks. In addition, draw-downs were made by the government of Kiribati to finance budgetary shortfalls during this period.
