Mali was once part of three famed West African empires which controlled trans-Saharan trade in gold, salt, slaves, and other precious commodities majorly during the reign of Mansa Musa from c. 1312 – c. 1337. These Sahelian kingdoms had neither rigid geopolitical boundaries nor rigid ethnic identities. The earliest of these empires was the Ghana Empire, which was dominated by the Soninke, a Mande-speaking people. The empire expanded throughout West Africa from the 8th century until 1078, when it was conquered by the Almoravids.

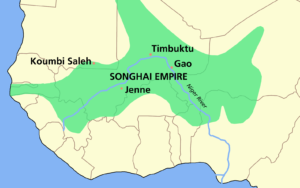
The Mali Empire later formed on the upper Niger River, and reached the height of power in the 14th century. Under the Mali Empire, the ancient cities of Djenné and Timbuktu were centers of both trade and Islamic learning. The empire later declined as a result of internal intrigue, ultimately being supplanted by the Songhai Empire. The Songhai people originated in current northwestern Nigeria. The Songhai had long been a major power in West Africa subject to the Mali Empire’s rule.
In the late 14th century, the Songhai gradually gained independence from the Mali Empire and expanded, ultimately subsuming the entire eastern portion of the Mali Empire. The Songhai Empire’s eventual collapse was largely the result of a Moroccan invasion in 1591, under the command of Judar Pasha. The fall of the Songhai Empire marked the end of the region’s role as a trading crossroads. Following the establishment of sea routes by the European powers, the trans-Saharan trade routes lost significance.
One of the worst famines in the region’s recorded history occurred in the 18th century. According to John Iliffe, “The worst crises were in the 1680s, when famine extended from the Senegambian coast to the Upper Nile and ‘many sold themselves for slaves, only to get a sustenance’, and especially in 1738–1756, when West Africa’s greatest recorded subsistence crisis, due to drought and locusts, reportedly killed half the population of Timbuktu.”
French Colonial Rule:
Mali fell under the control of France during the late 19th century. By 1905, most of the area was under firm French control as a part of French Sudan. In early 1959, French Sudan (which changed its name to the Sudanese Republic) and Senegal united to become the Mali Federation. The Mali Federation gained independence from France on 20 June 1960.
Senegal withdrew from the federation in August 1960, which allowed the Sudanese Republic to become the independent Republic of Mali on 22 September 1960, and that date is now the country’s Independence Day. Modibo Keïta was elected the first president.

Keïta quickly established a one-party state, adopted an independent African and socialist orientation with close ties to the East, and implemented extensive nationalization of economic resources. In 1960, the population of Mali was reported to be about 4.1 million.
Moussa Traoré:
On 19 November 1968, following progressive economic decline, the Keïta regime was overthrown in a bloodless military coup led by Moussa Traoré, a day which is now commemorated as Liberation Day. The subsequent military-led regime, with Traoré as president, attempted to reform the economy. His efforts were frustrated by political turmoil and a devastating drought between 1968 and 1974, in which famine killed thousands of people. The Traoré regime faced student unrest beginning in the late 1970s and three coup attempts. The Traoré regime repressed all dissenters until the late 1980s.
