In the second decade of the 21st century, the Portuguese economy suffered its most severe recession since the 1970s, resulting in the country having to be bailed out by the European Commission, European Central Bank and International Monetary Fund (IMF). The bailout, agreed to in 2011, required Portugal to enter into a range of austerity measures in exchange for funding support of €78,000,000,000. In May 2014, the country exited the bailout but reaffirmed its commitment to maintaining its reformist momentum.
Transportation:
By the early-1970s, Portugal’s fast economic growth with increasing consumption and purchase of new automobiles set the priority for improvements in transportation. Again in the 1990s, after joining the European Economic Community, the country built many new motorways. Today, the country has a 68,732 km (42,708 mi) road network, of which almost 3,000 km (1,864 mi) are part of system of 44 motorways.
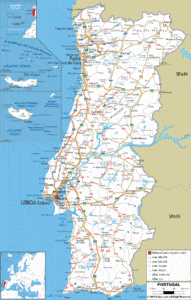
Continental Portugal’s 89,015 km2 (34,369 sq mi) territory is serviced by four international airports located near the principal cities of Lisbon, Porto, Faro and Beja. Lisbon’s geographical position makes it a stopover for many foreign airlines at several airports within the country. The primary flag-carrier is TAP Air Portugal, although many other domestic airlines provide services within and without the country. Currently, the most important airports are in Lisbon, Porto, Faro, Funchal (Madeira), and Ponta Delgada (Azores), managed by the national airport authority group ANA – Aeroportos de Portugal. One other important airport is the Aeroporto Internacional das Lajes on the island of Terceira in the Azores. This airport serves as one of two international airports serving countries outside the European Union for all nine islands of the Azores. It also serves as a military air base for the United States Air Force. The base remains in use to the present day.

A national railway system that extends throughout the country and into Spain, is supported and administered by Comboios de Portugal (CP). Rail transport of passengers and goods is derived using the 2,791 km (1,734 mi) of railway lines currently in service, of which 1,430 km (889 mi) are electrified and about 900 km (559 mi) allow train speeds greater than 120 km/h (75 mph).
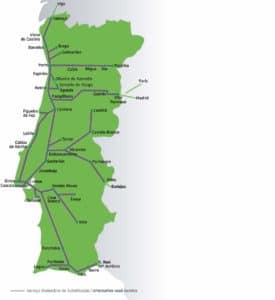
The major seaports are located in Sines, Lisbon, Leixões, Setúbal, Aveiro, Figueira da Foz, and Faro.
The two largest metropolitan areas have subway systems: Lisbon Metro and Metro Sul do Tejo in the Lisbon metropolitan area and Porto Metro in the Porto Metropolitan Area, each with more than 35 km (22 mi) of lines.

In Portugal, Lisbon tram services have been supplied by the Companhia de Carris de Ferro de Lisboa (Carris), for over a century. All major cities and towns have their own local urban transport network, as well as taxi services.
Flag of Portugal:
The flag of Portugal is a rectangular bicolor with a field divided into green on the hoist, and red on the fly. The lesser version of the national coat of arms (armillary sphere and Portuguese shield) is centered over the color boundary at equal distance from the upper and lower edges. On 30 June 1911, less than a year after the downfall of the constitutional monarchy, this design was officially adopted for the new national flag of the First Portuguese Republic, after selection by a special commission whose members included Columbano Bordalo Pinheiro, João Chagas and Abel Botelho.
