In April 2008 Serbia was invited to join the Intensified Dialogue program with NATO, despite the diplomatic rift with the alliance over Kosovo. Serbia officially applied for membership in the European Union on 22 December 2009, and received candidate status on 1 March 2012, following a delay in December 2011. Following a positive recommendation of the European Commission and European Council in June 2013, negotiations to join the EU commenced in January 2014.

Since Aleksandar Vučić came to power, Serbia has suffered from democratic backsliding into authoritarianism, followed by a decline in media freedom and civil liberties. Massive anti-government protests began in 2018 and continued into 2020, making them one of Europe’s longest-running protests. After the COVID-19 pandemic spread to Serbia in March 2020, a state of emergency was declared and a curfew was introduced for the first time in Serbia since World War II. In January and February 2021 Serbia carried the second-fastest vaccine rollout in Europe.
Geography:
A landlocked country situated at the crossroads between Central and Southern Europe, Serbia is located in the Balkan peninsula and the Pannonian Plain. The country covers a total of 88,361 km2 (including Kosovo), which places it at 113th place in the world; with Kosovo excluded, the total area is 77,474 km2, which would make it 117th. The Pannonian Plain covers the northern third of the country (Vojvodina and Mačva) while the easternmost tip of Serbia extends into the Wallachian Plain. The terrain of the central part of the country, with the region of Šumadija at its heart, consists chiefly of hills traversed by rivers. Mountains dominate the southern third of Serbia. Dinaric Alps stretch in the west and the southwest, following the flow of the rivers Drina and Ibar. The Carpathian Mountains and Balkan Mountains stretch in a north–south direction in eastern Serbia.
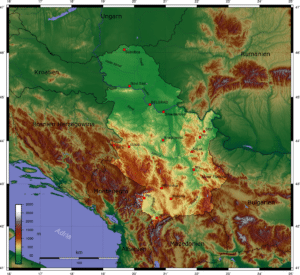
Ancient mountains in the southeast corner of the country belong to the Rilo-Rhodope Mountain system. Elevation ranges from the Midžor peak of the Balkan Mountains at 2,169 meters (7,116 feet) (the highest peak in Serbia, excluding Kosovo) to the lowest point of just 17 meters (56 feet) near the Danube river at Prahovo. The largest lake is Đerdap Lake (163 square kilometers) and the longest river passing through Serbia is the Danube.
Economy:
Serbia has an emerging market economy in upper-middle income range. The economy is dominated by services which accounts for 67.9% of GDP, followed by industry with 26.1% of GDP, and agriculture at 6% of GDP. The official currency of Serbia is Serbian dinar, and the central bank is National Bank of Serbia.

Serbia has an unfavorable trade balance: imports exceed exports by 25%. Serbia’s exports, however, recorded a steady growth in last couple of years reaching $19.2 billion in 2018. The country has free trade agreements with the EFTA and CEFTA, a preferential trade regime with the European Union, a Generalized System of Preferences with the United States, and individual free trade agreements with Russia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, and Turkey.
