Serbia is among the world’s largest producer of plums as of 2018, which is considered the national fruit of Serbia.
Serbia is among the world’s largest producer of raspberries as of 2016.

Serbia is one of the largest provider of frozen fruit to the EU (largest to the French market, and 2nd largest to the German market).
Agricultural production is most prominent in Vojvodina on the fertile Pannonian Plain.
Main industrial sectors include: automotive, mining, non-ferrous metals, food-processing, electronics, pharmaceuticals, clothes.
Transportation:
Serbia has a strategic transportation location since the country’s backbone, Morava Valley, represents the easiest land route from continental Europe to Asia Minor and the Near East.
Serbian road network carries the bulk of traffic in the country. Total length of roads is 45,419 km of which 962 km are “class-IA state roads” (i.e. motorways); 4,517 km are “class-IB state roads” (national roads); 10,941 km are “class-II state roads” (regional roads) and 23,780 km are “municipal roads”. The road network, except for the most of class-IA roads, are of comparatively lower quality to the Western European standards because of lack of financial resources for their maintenance in the last 20 years.
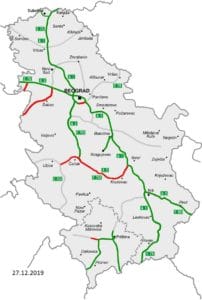
Over 300 kilometers of new motorways has been constructed in the last decade and additional 154 kilometers are currently under construction. Coach transport is very extensive: almost every place in the country is connected by bus, from largest cities to the villages; in addition there are international routes (mainly to countries of Western Europe with large Serb diaspora).
Serbia has 3,819 kilometers of rail tracks, of which 1,279 are electrified and 283 kilometers are double-track railroad. Although still a major mode of freight transportation, railroads face increasing problems with the maintenance of the infrastructure and lowering speeds. Rail services are operated by Srbija Voz (passenger transport) and Srbija Kargo (freight transport).
There are three airports with regular passenger traffic. Belgrade Nikola Tesla Airport served 6.2 million passengers in 2019 and is a hub of flagship carrier Air Serbia which flies to 59 destinations in 32 countries and carried some 2.8 million passengers in 2019. Niš Constantine the Great Airport and Morava Airport are mainly catering low-cost airlines but also serving as secondary Air Serbia hubs.

Serbia has a developed inland water transport since there are 1,716 kilometers of navigable inland waterways (1,043 km of navigable rivers and 673 km of navigable canals), which are almost all located in northern third of the country. The most important inland waterway is the Danube (part of Pan-European Corridor VII). Other navigable rivers include Sava, Tisza, Begej and Timiş River, all of which connect Serbia with Northern and Western Europe through the Rhine–Main–Danube Canal and North Sea route, to Eastern Europe via the Tisza, Begej and Danube Black Sea routes, and to Southern Europe via the Sava river. More than 8 million tons of cargo were transported on Serbian rivers and canals in 2018 while the largest river ports are: Novi Sad, Belgrade, Pančevo, Smederevo, Prahovo and Šabac.
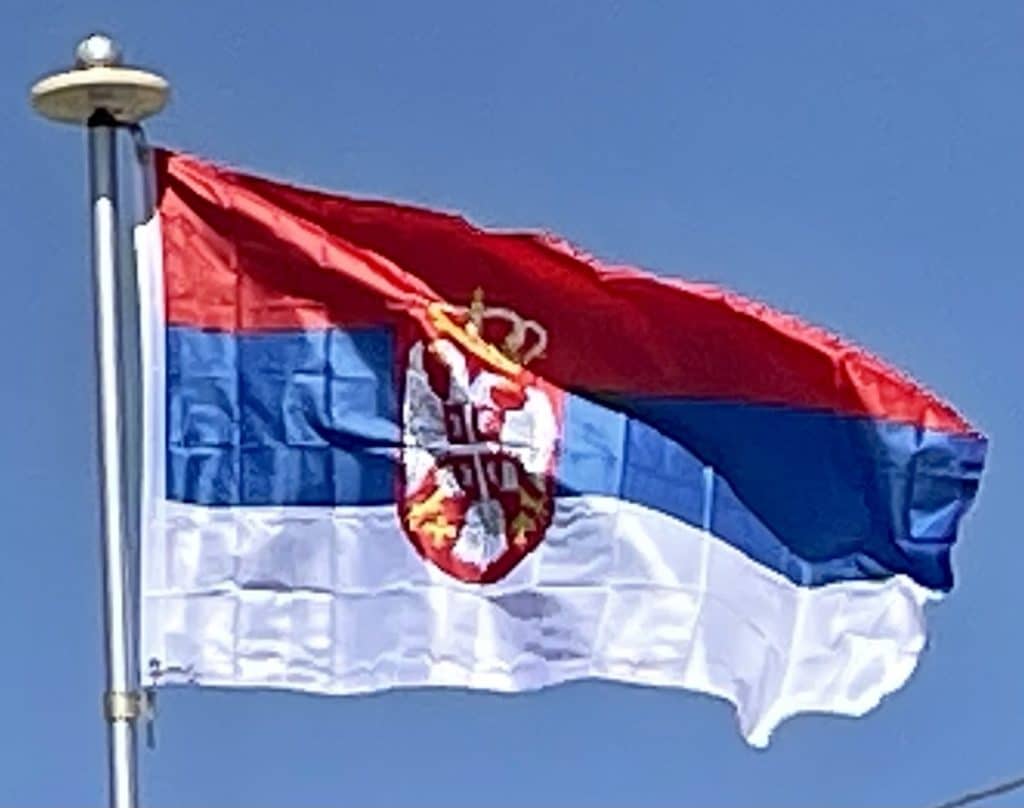
Flag of Serbia:
The flag of Serbia, also known as the Tricolour, is a tricolor consisting of three equal horizontal bands, red on the top and blue in the middle (Kingdom), and white on the bottom (Empire). The same tricolor, in altering variations, has been used since the 19th century as the flag of the state of Serbia and the Serbian nation. The current form of the flag was officially adopted on 11 November 2010.
