Introduction:
Saint Kitts and Nevis, officially known as the Federation of Saint Christopher and Nevis, is an island country in the West Indies. Located in the Leeward Islands chain of the Lesser Antilles, it is the smallest sovereign state in the Western Hemisphere, in both area and population. The country is a Commonwealth realm, with Elizabeth II as Queen and head of state. It is the only federation in the Caribbean.
The capital city is Basseterre, located on the larger island of Saint Kitts. Basseterre is also the main port for both passenger entry (via cruise ships) and cargo. The smaller island of Nevis lies approximately 3 km (2 mi) to the southeast of Saint Kitts, across a shallow channel called The Narrows.
The British dependency of Anguilla was historically also a part of this union, which was then known collectively as Saint Christopher-Nevis-Anguilla. However, Anguilla chose to secede from the union and remains a British overseas territory. To the north-northwest lie the islands of Sint Eustatius, Saba, Saint Barthélemy, Saint-Martin/Sint Maarten and Anguilla. To the east and northeast are Antigua and Barbuda, and to the southeast is the small uninhabited island of Redonda (part of Antigua and Barbuda) and the island of Montserrat.

Saint Kitts and Nevis were among the first islands in the Caribbean to be colonized by Europeans. Saint Kitts was home to the first British and French colonies in the Caribbean, and thus has also been titled “The Mother Colony of the West Indies”. It is also the most recent British territory in the Caribbean to become independent, gaining independence in 1983.
History:
Pre-Colonial Period:
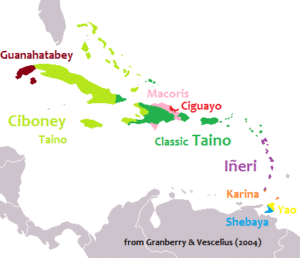
The name of the first inhabitants, pre-Arawakan peoples who settled the islands perhaps as early as 3000 years ago, is not known. They were followed by the Arawak peoples, or Taíno, about 1000 BC. The warlike Island Caribs invaded about 800 AD.
European Arrival and Early Colonial Period:
Christopher Columbus was the first European to sight the islands in 1493. The first settlers were the English in 1623, led by Thomas Warner, who established a settlement at Old Road Town on the west coast of St Kitts after achieving an agreement with the Carib chief Ouboutou Tegremante. The French later also settled on St Kitts in 1625 under Pierre Belain d’Esnambuc. As a result, both parties agreed to partition the island into French and English sectors. From 1628 onward the English also began settling on Nevis.
The French and English, intent on self-enrichment through exploitation of the island’s natural resources, soon encountered resistance, with the native Caribs (Kalinago) waging war throughout the first three years of the settlements’ existence. The Europeans thus resolved to rid themselves of this problem once and for all. To facilitate this objective, an ideological campaign was waged by colonial chroniclers, dating back to the Spanish, as they produced literature which systematically denied Kalinago humanity (a literary tradition carried through the late-seventeenth century by such authors as Jean-Baptiste du Tertre and Pere Labat). In 1626 the Anglo-French settlers joined forces to massacre the Kalinago at a place that became known as Bloody Point, allegedly to pre-empt an imminent Carib plan to expel or kill all European settlers. With the native population thus pacified, the English and French began to establish large sugar plantations which were worked by vast numbers of imported African slaves. This system created enormous wealth for the planter-colonists whilst also drastically changing the islands’ demographics as black slaves soon came to outnumber Europeans by some margin.
