Israel
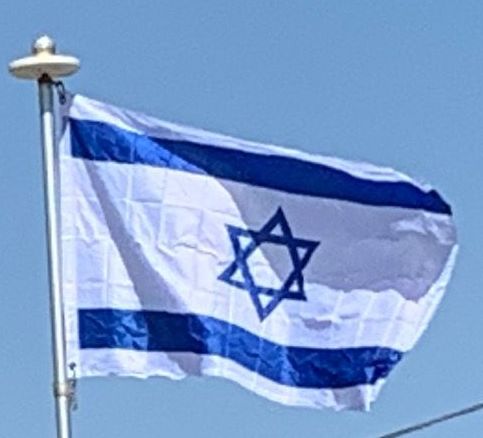
The flag of Israel was adopted on 28 October 1948, five months after the establishment of the State of Israel. It depicts a blue Star of David on a white background, between two horizontal blue stripes.
The blue colour is described as “dark sky-blue”, and varies from flag to flag, ranging from a hue of pure blue, sometimes shaded almost as dark as navy blue, to hues about 75% toward pure cyan and shades as light as very light blue.
The flag was designed for the Zionist Movement in 1891. The basic design recalls the Tallit (טַלִּית), the Jewish prayer shawl, which is white with black or blue stripes. The symbol in the center represents the Star of David (Magen David, מָגֵן דָּוִד), a Jewish symbol dating from late medieval Prague, which was adopted by the First Zionist Congress in 1897.