

The UK has an external debt of $9.6 trillion dollars, which is the second-highest in the world after the US. As a percentage of GDP, external debt is 408 per cent, which is the third-highest in the world after Luxembourg and Iceland.
A radial road network totals 29,145 miles (46,904 km) of main roads, 2,173 miles (3,497 km) of motorways and 213,750 miles (344,000 km) of paved roads. The M25, encircling London, is the largest and busiest bypass in the world. In 2009 there were a total of 34 million licensed vehicles in Great Britain.
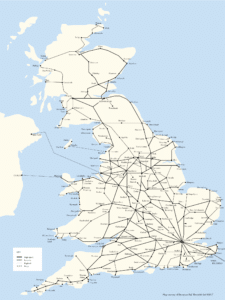
The rail network in the UK is the oldest such network in the world. The system consists of five high-speed main lines (the West Coast, East Coast, Midland, Great Western and Great Eastern), which radiate from London to the rest of the country, augmented by regional rail lines and dense commuter networks within the major cities. High Speed 1 is operationally separate from the rest of the network. The world’s first passenger railway running on steam was the Stockton and Darlington Railway, opened on 27 September 1825. Just under five years later the world’s first intercity railway was the Liverpool and Manchester Railway, designed by George Stephenson and opened by the Prime Minister, the Duke of Wellington on 15 September 1830. The network grew rapidly as a patchwork of literally hundreds of separate companies during the Victorian era.
The UK has a railway network of 10,072 miles (16,209 km) in Great Britain and 189 miles (304 km) in Northern Ireland. Railways in Northern Ireland are operated by NI Railways, a subsidiary of state-owned Translink. In Great Britain, the British Rail network was privatized between 1994 and 1997, which was followed by a rapid rise in passenger numbers. The UK was ranked eighth among national European rail systems in the 2017 European Railway Performance Index assessing intensity of use, quality of service and safety. Network Rail owns and manages most of the fixed assets (tracks, signals etc.). HS2, a new high-speed railway line, is estimated to cost £56 billion. Crossrail, under construction in London, is Europe’s largest construction project with a £15 billion projected cost.
In the year from October 2009 to September 2010 UK airports handled a total of 211.4 million passengers. In that period the three largest airports were London Heathrow Airport (65.6 million passengers), Gatwick Airport (31.5 million passengers) and London Stansted Airport (18.9 million passengers). London Heathrow Airport, located 15 miles (24 km) west of the capital, has the most international passenger traffic of any airport in the world and is the hub for the UK flag carrier British Airways, as well as Virgin Atlantic.