Meanwhile, conservationists including Aldo Leopold helped re-establish the state’s forests during the early 20th century, paving the way for a more renewable lumber and paper milling industry as well as promoting recreational tourism in the northern woodlands. Manufacturing also boomed in Wisconsin during the early 20th century, driven by an immense immigrant workforce arriving from Europe. Industries in cities like Milwaukee ranged from brewing and food processing to heavy machine production and tool-making, leading Wisconsin to rank 8th among U.S. states in total product value by 1910.

20th Century:
In the immediate aftermath of World War II, citizens of Wisconsin were divided over things such as the creation of the United Nations, support for the European recovery, and the growth of the Soviet Union‘s power. However, when Europe divided into Communist and capitalist camps and the Communist revolution in China succeeded in 1949, public opinion began to move towards support for the protection of democracy and capitalism against Communist expansion.
The state became a leader in welfare reform under Republican Governor Tommy Thompson during the 1990s. The state’s economy also underwent further transformations towards the close of the 20th century, as heavy industry and manufacturing declined in favor of a service economy based on medicine, education, agribusiness, and tourism.
21st Century:
In 2011, Wisconsin became the focus of some controversy when newly elected governor Scott Walker proposed, successfully passed, and enacted the 2011 Wisconsin Act 10, which made large changes in the areas of collective bargaining, compensation, retirement, health insurance, and sick leave of public sector employees, among other changes. A series of major protests by union supporters took place that year in response to the changes, and Walker survived a recall election held the next year, becoming the first governor in United States history to do so. Walker enacted other bills promoting conservative governance, such as a right-to-work law, abortion restrictions, and legislation removing certain gun controls.
Geography:
Wisconsin is bordered by the Montreal River; Lake Superior and Michigan to the north; by Lake Michigan to the east; by Illinois to the south; and by Iowa to the southwest and Minnesota to the northwest. A border dispute with Michigan was settled by two cases, both Wisconsin v. Michigan, in 1934 and 1935. The state’s boundaries include the Mississippi River and St. Croix River in the west, and the Menominee River in the northeast.
With its location between the Great Lakes and the Mississippi River, Wisconsin is home to a wide variety of geographical features. The state is divided into five distinct regions.
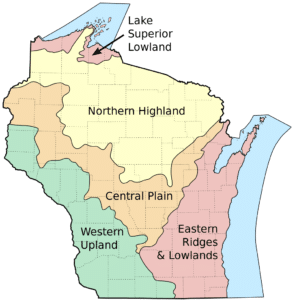
In the north, the Lake Superior Lowland occupies a belt of land along Lake Superior. Just to the south, the Northern Highland has massive mixed hardwood and coniferous forests including the 1,500,000 acres Chequamegon-Nicolet National Forest, as well as thousands of glacial lakes, and the state’s highest point, Timms Hill.

