Introduction:
Yukon is the smallest and westernmost of Canada’s three territories (the other two are the Northwest Territories and Nunavut). It has the smallest population of any province or territory in Canada, with 35,874 people, although it has the largest city in any of the three territories. Whitehorse is the territorial capital and Yukon’s only city.
Yukon was split from the Northwest Territories in 1898 and was originally named the Yukon Territory. The federal government’s Yukon Act, which received royal assent on March 27, 2002, established Yukon as the territory’s official name, though Yukon Territory is also still popular in usage and Canada Post continues to use the territory’s internationally approved postal abbreviation of YT. Though officially bilingual (English and French), the Yukon government also recognizes First Nations languages.
At 5,959 m (19,551 ft), Yukon’s Mount Logan, in Kluane National Park and Reserve, is the highest mountain in Canada and the second-highest on the North American continent (after Denali in the U.S. state of Alaska). Most of Yukon has a subarctic climate, characterized by long, cold winters and brief, warm summers. The Arctic Ocean coast has a tundra climate.
Notable rivers include the Yukon River (after which the territory was named), as well as the Pelly, Stewart, Peel, White, and Tatshenshini rivers.
Etymology:
The territory is named after the Yukon River, the longest river in Yukon. The name itself is from a contraction of the words in the Gwich’in phrase chųų gąįį han, which means white water river and refers to “the pale color” of glacial runoff in the Yukon River.
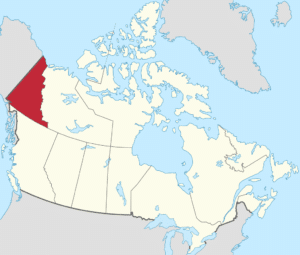
Geography:
The territory is the approximate shape of a right triangle, bordering the U.S. state of Alaska to the west and northwest for 1,210 km (752 mi) mostly along longitude 141° W, the Northwest Territories to the east and British Columbia to the south. Its northern coast is on the Beaufort Sea. Its ragged eastern boundary mostly follows the divide between the Yukon Basin and the Mackenzie River drainage basin to the east in the Mackenzie mountains.

Most of the territory is in the watershed of its namesake, the Yukon River. The southern Yukon is dotted with a large number of large, long and narrow glacier-fed alpine lakes, most of which flow into the Yukon River system. The larger lakes include Teslin Lake, Atlin Lake, Tagish Lake, Marsh Lake, Lake Laberge, Kusawa Lake and Kluane Lake. Bennett Lake on the Klondike Gold Rush trail is a lake flowing into Nares Lake, with the greater part of its area within Yukon.
Other watersheds in the territory include the Mackenzie River, the Peel Watershed and the Alsek–Tatshenshini, and a number of rivers flowing directly into the Beaufort Sea. The two main Yukon rivers flowing into the Mackenzie in the Northwest Territories are the Liard River in the southeast and the Peel River and its tributaries in the northeast.
Canada’s highest point, Mount Logan (5,959 m or 19,551 ft), is in the territory’s southwest. Mount Logan and a large part of Yukon’s southwest are in Kluane National Park and Reserve, a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Other national parks include Ivvavik National Park and Vuntut National Park in the north.
History:
Long before the arrival of Europeans, central and southern Yukon was populated by First Nations people, and the area escaped glaciation. Sites of archaeological significance in Yukon hold some of the earliest evidence of the presence of human habitation in North America. The sites safeguard the history of the first people and the earliest First Nations of the Yukon.
