Introduction:
New Mexico is a state in the Southwestern Region of the United States of America. It is one of the Mountain States and shares the Four Corners region with Utah, Colorado, and Arizona; its other neighboring states are Oklahoma to the northeast, Texas to the east-southeast, and the Mexican states of Chihuahua to the south and Sonora to the southwest.
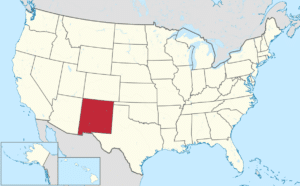
Its capital and cultural center is Santa Fe, while its largest city is Albuquerque.

The economy of New Mexico is dependent on oil drilling, mineral extraction, dryland farming, cattle ranching, lumber milling, and retail trade.
Inhabited by Native Americans for thousands of years before European exploration, it was colonized by the Spanish in 1598 as part of the Imperial Spanish viceroyalty of New Spain.
Origin of the Name:
New Mexico received its name long before the present-day nation of Mexico won independence from Spain and adopted that name in 1821. Spanish explorers recorded this region as New Mexico (Nuevo México in Spanish) in 1563. In 1581, the Chamuscado and Rodríguez Expedition named the region north of the Rio Grande “San Felipe del Nuevo México”.
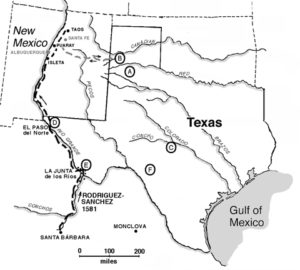
The Spaniards hoped to find wealthy Mexican Indian cultures there similar to those of the Aztec (Mexica) Empire of the Valley of Mexico. The indigenous cultures of New Mexico, however, proved to be unrelated to the Aztecs, and were not wealthy. Before statehood, the name “New Mexico” was applied to various configurations of the U.S. Territory, to a Mexican state, and to a province of New Spain, all in the same general area, but of varying extensions.
Geography:
The New Mexican landscape ranges from wide, rose-colored deserts to broken mesas to high, snow-capped peaks. Despite New Mexico’s arid image, heavily forested mountain wildernesses cover a significant portion of the state, especially towards the north. The Sangre de Cristo Mountains, the southernmost part of the Rocky Mountains, run roughly north–south along the east side of the Rio Grande in the rugged, pastoral north.

The most important of New Mexico’s rivers are the Rio Grande, Pecos, Canadian, San Juan, and Gila. The Rio Grande is tied for the fourth-longest river in the United States.
The U.S. government protects millions of acres of New Mexico as national forests, national parks and national monuments.

The climate of New Mexico is generally semiarid to arid, though areas of continental and alpine climates exist, and its territory is mostly covered by mountains, high plains, and desert. The Great Plains (High Plains) are in Eastern New Mexico, similar to the Colorado high plains in eastern Colorado. The two states share similar terrain, with both having plains, mountains, basins, mesas, and desert lands.
History:
Pre-History:
The first known inhabitants of New Mexico were members of the Clovis culture of Paleo-Indians.
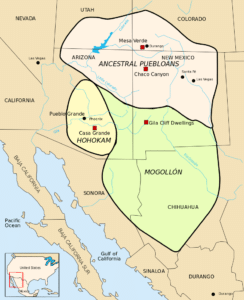
Later inhabitants include American Indians of the Mogollon and Ancestral Pueblo peoples cultures. By the time of European contact in the 16th century, the region was settled by the villages of the Pueblo peoples and groups of Navajo, Apache, and Ute.
European Exploration:
Francisco Vásquez de Coronado assembled an enormous expedition at Compostela in 1540–1542 to explore and find the mythical Seven Golden Cities of Cibola as described by Fray Marcos de Niza. The name Nuevo México was first used by a seeker of gold mines named Francisco de Ibarra, who explored far to the north of New Spain in 1563 and reported his findings as being in “a New Mexico”.
