In addition to the issues of Quebec sovereignty, a number of crises shook Canadian society in the late 1980s and early 1990s. These included the explosion of Air India Flight 182 in 1985, the largest mass murder in Canadian history; the École Polytechnique massacre in 1989, a university shooting targeting female students; and the Oka Crisis of 1990, the first of a number of violent confrontations between the government and indigenous groups. Canada also joined the Gulf War in 1990 as part of a U.S.-led coalition force and was active in several peacekeeping missions in the 1990s, including the UNPROFOR mission in the former Yugoslavia.
Canada sent troops to Afghanistan in 2001, but declined to join the U.S.-led invasion of Iraq in 2003. In 2011, Canadian forces participated in the NATO-led intervention into the Libyan Civil War, and also became involved in battling the Islamic State insurgency in Iraq in the mid-2010s.
Geography:
Canada occupies much of the continent of North America, sharing land borders with the contiguous United States to the south, and the U.S. state of Alaska to the northwest. Canada stretches from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west; to the north lies the Arctic Ocean. Greenland is to the northeast and to the southeast Canada shares a maritime boundary with the Republic of France’s overseas collectivity of Saint Pierre and Miquelon, the last vestige of New France. By total area (including its waters), Canada is the second-largest country in the world, after Russia. By land area alone, however, Canada ranks fourth, the difference being due to it having the world’s largest proportion of fresh water lakes. Of Canada’s thirteen provinces and territories, only two are landlocked (Alberta and Saskatchewan) while the other eleven all directly border one of three oceans.
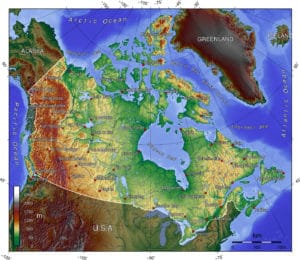
Canada is home to the world’s northernmost settlement, Canadian Forces Station Alert, on the northern tip of Ellesmere Island which lies 508 miles from the North Pole. Much of the Canadian Arctic is covered by ice and permafrost. Canada has the longest coastline in the world, with a total length of 151,019 miles; additionally, its border with the United States is the world’s longest land border, stretching (5,525 miles. Three of Canada’s arctic islands, Baffin Island, Victoria Island and Ellesmere Island, are among the ten largest in the world.
Since the end of the last glacial period, Canada has consisted of eight distinct forest regions, including extensive boreal forest on the Canadian Shield. 42 percent of the land acreage of Canada is covered by forests, approximately 8 percent of the world’s forested land, made up mostly of spruce, poplar and pine. Canada has over 2,000,000 lakes—563 greater than 39 square miles which is more than any other country, containing much of the world’s fresh water. There are also fresh-water glaciers in the Canadian Rockies and the Coast Mountains.
Economy:
Canada is the world’s tenth-largest economy as of 2018, with a nominal GDP of approximately US$1.73 trillion. It is a member of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) and the Group of Eight (G8), and is one of the world’s top ten trading nations, with a highly globalized economy. Canada is a mixed economy, ranking above the U.S. and most western European nations on The Heritage Foundation’s index of economic freedom, and experiencing a relatively low level of income disparity. The country’s average household disposable income per capita is “well above” the OECD average. Furthermore, the Toronto Stock Exchange is the seventh-largest stock exchange in the world by market capitalization, listing over 1,500 companies with a combined market capitalization of over US$2 trillion as of 2015.
