Introduction:
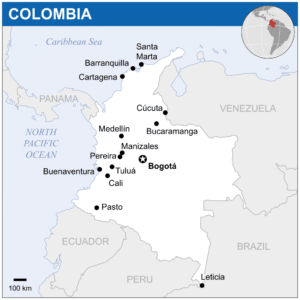
Colombia, officially the Republic of Colombia is a country largely situated in the north of South America, with land and territories in North America. Colombia is bounded on the north by the Caribbean Sea, the northwest by Panama, the south by both Ecuador and Peru, the east by Venezuela, the southeast by Brazil, and the west by the Pacific. It comprises thirty-two departments, with the capital in Bogotá.
Colombia is ethnically and linguistically diverse, with its rich cultural heritage reflecting influences by various Amerindian civilizations, European settlement, forced African labor, and immigration from Europe and the greater Middle East. Urban centers are concentrated in the Andean highlands and the Caribbean coast.
Colombia has been inhabited by various American Indian peoples since at least 12,000 BCE, including the Muisca, Quimbaya, and the Tairona, along with the Inca Empire that expanded to the southwest of the country. Spaniards arrived in 1499 and by the mid-16th century annexed part of the region, establishing the New Kingdom of Granada, with Santafé de Bogotá as its capital. Independence from Spain was achieved in 1819, but by 1830 the Gran Colombia Federation was dissolved, with what is now Colombia and Panama emerging as the Republic of New Granada. The new sovereign state experimented with federalism as the Granadine Confederation (1858), and then the United States of Colombia (1863), before the Republic of Colombia was finally declared in 1886. Panama seceded in 1903, leading to Colombia’s present borders. Beginning in the 1960s, the country suffered from an asymmetric low-intensity armed conflict and political violence, both of which escalated in the 1990s. Since 2005, there has been significant improvement in security, stability, and rule of law.
Colombia has the second-highest biodiversity in the world and is one of the world’s 17 mega-diverse countries; its territory encompasses Amazon rain forest, highlands, grasslands, deserts, and islands and coastlines along both the Atlantic and Pacific.
Colombia is the only NATO Global Partner in Latin America. It is part of the CIVETS group of leading emerging markets and a member of the UN, the WTO, the OAS, the Pacific Alliance, an associate member of Mercosur and other international organizations. Colombia’s diversified economy is the third largest in South America, with macroeconomic stability and favorable long-term growth prospects.
Etymology:
The name “Colombia” is derived from the last name of the navigator Christopher Columbus (Italian: Cristoforo Colombo, Spanish: Cristóbal Colón). It was conceived by the Venezuelan revolutionary Francisco de Miranda as a reference to all the New World, but especially to those portions under Spanish law (by then from the Mississippi River to Patagonia). The name was later adopted by the Republic of Colombia of 1819, formed from the territories of the old Viceroyalty of New Granada (modern-day Colombia, Panama, Venezuela, Ecuador, and northwest Brazil).
When Venezuela, Ecuador, and Cundinamarca came to exist as independent states, the former Department of Cundinamarca adopted the name “Republic of New Granada”. New Granada officially changed its name in 1858 to the Granadine Confederation. In 1863 the name was again changed, this time to United States of Colombia, before finally adopting its present name – the Republic of Colombia – in 1886.
History:
Pre-Columbian Era:
Owing to its location, the present territory of Colombia was a corridor of early human civilization from Mesoamerica and the Caribbean to the Andes and Amazon basin. The oldest archaeological finds are from the Pubenza and El Totumo sites in the Magdalena Valley 100 kilometres (62 mi) southwest of Bogotá. These sites date from the Paleoindian period (18,000–8000 BCE). At Puerto Hormiga and other sites, traces from the Archaic Period (~8000–2000 BCE) have been found. Vestiges indicate that there was also early occupation in the regions of El Abra and Tequendama in Cundinamarca. The oldest pottery discovered in the Americas, found at San Jacinto, dates to 5000–4000 BCE.
