A series of alternating military and civilian governments, often affected by economic instabilities, ruled Ghana from 1966 to 1981, ending with the ascension to power of Flight Lieutenant Jerry John Rawlings of the Provisional National Defence Council (PNDC) in 1981. These changes resulted in the suspension of the Constitution of Ghana in 1981, and the banning of political parties in Ghana. The economy soon declined, so Rawlings negotiated a structural adjustment plan changing many old economic policies, and economic growth soon recovered during the mid-1980s. A new Constitution of Ghana restoring multi-party system politics was promulgated in Ghanaian presidential election, 1992; Rawlings was elected as president of Ghana then, and again in Ghanaian general election, 1996.
21st Century:
Winning the 2000 Ghanaian elections, John Agyekum Kufuor of the New Patriotic Party (NPP) was sworn into office as president of Ghana on 7 January 2001, and attained the presidency again in the 2004 Ghanaian elections, thus also serving two terms (the term limit) as president of Ghana and thus marking the first time under the fourth republic that power was transferred from one legitimately elected head of state and head of government to another.
Nana Akufo-Addo, the ruling party candidate, was defeated in a very close election by John Atta Mills of the National Democratic Congress (NDC) following the Ghanaian presidential election, 2008. Mills died of natural causes and was succeeded by vice-president John Dramani Mahama on 24 July 2012.

Following the Ghanaian presidential election, 2012, John Dramani Mahama became President-elect and was inaugurated on 7 January 2013. Ghana was a stable democracy.
As a result of the Ghanaian presidential election, 2016, Nana Akufo-Addo became President-elect and was inaugurated as the fifth President of the Fourth Republic of Ghana and eighth President of Ghana on 7 January 2017.
Geography:
Ghana is located on the Gulf of Guinea, only a few degrees north of the Equator, therefore giving it a warm climate. The Prime Meridian passes through Ghana, specifically through the industrial port town of Tema.
Grasslands mixed with south coastal shrublands and forests dominate Ghana, with forest extending northward from the south-west coast of Ghana on the Gulf of Guinea in the Atlantic Ocean 320 kilometres (200 miles) and eastward for a maximum of about 270 kilometres (170 miles) with the Kingdom of Ashanti or the southern part of Ghana being a primary location for mining of industrial minerals and timber.
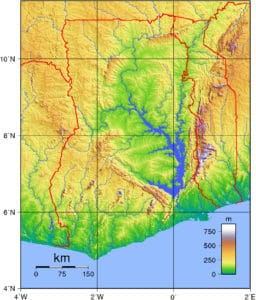
Ghana encompasses plains, waterfalls, low hills, rivers, Lake Volta, the world’s largest artificial lake, Dodi Island and Bobowasi Island on the south Atlantic Ocean coast of Ghana. The northernmost part of Ghana is Pulmakong and the southernmost part of Ghana is Cape Three Points.
Economy:
Ghana is an average natural resource enriched country possessing industrial minerals, hydrocarbons and precious metals. It is an emerging designated digital economy with mixed economy hybridization and an emerging market with 8.7% GDP growth in 2012. It has an economic plan target known as the “Ghana Vision 2020”. This plan envisions Ghana as the first African country to become a developed country between 2020 and 2029 and a newly industrialized country between 2030 and 2039. This excludes fellow Group of 24 member and Sub-Saharan African country South Africa, which is a newly industrialized country.
