In 1920, following World War I, the area of the Mutasarrifate, plus some surrounding areas which were predominantly Shia and Sunni, became a part of the state of Greater Lebanon under the French Mandate of Syria and Lebanon. Around 100,000 people in Beirut and Mount Lebanon died of starvation during World War I. In the first half of 1920, Lebanese territory was claimed as part of the Arab Kingdom of Syria, but shortly the Franco-Syrian War resulted in Arab defeat and capitulation of the Hashemites.
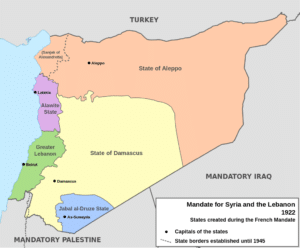
On 1 September 1920, France reestablished Greater Lebanon after the Moutasarrifiya rule removed several regions belonging to the Principality of Lebanon and gave them to Syria. Lebanon was a largely Christian country (mainly Maronite territory with some Greek Orthodox enclaves) but it also included areas containing many Muslims and Druze. On 1 September 1926, France formed the Lebanese Republic. A constitution was adopted on 25 May 1926 establishing a democratic republic with a parliamentary system of government.
Independence from France:
Lebanon gained a measure of independence while France was occupied by Germany. General Henri Dentz, the Vichy High Commissioner for Syria and Lebanon, played a major role in the independence of the nation. The Vichy authorities in 1941 allowed Germany to move aircraft and supplies through Syria to Iraq where they were used against British forces. The United Kingdom, fearing that Nazi Germany would gain full control of Lebanon and Syria by pressure on the weak Vichy government, sent its army into Syria and Lebanon.

After the fighting ended in Lebanon, General Charles de Gaulle visited the area. Under political pressure from both inside and outside Lebanon, de Gaulle recognized the independence of Lebanon. On 26 November 1941, General Georges Catroux announced that Lebanon would become independent under the authority of the Free French government. Elections were held in 1943 and on 8 November 1943 the new Lebanese government unilaterally abolished the mandate. The French reacted by imprisoning the new government. In the face of international pressure, the French released the government officials on 22 November 1943. The allies occupied the region until the end of World War II.

Following the end of World War II in Europe the French mandate may be said to have been terminated without any formal action on the part of the League of Nations or its successor the United Nations. The mandate was ended by the declaration of the mandatory power, and of the new states themselves, of their independence, followed by a process of piecemeal unconditional recognition by other powers, culminating in formal admission to the United Nations. Article 78 of the UN Charter ended the status of tutelage for any member state: “The trusteeship system shall not apply to territories which have become Members of the United Nations, relationship among which shall be based on respect for the principle of sovereign equality.” So when the UN officially came into existence on 24 October 1945, after ratification of the United Nations Charter by the five permanent members, as both Syria and Lebanon were founding member states, the French mandate for both was legally terminated on that date and full independence attained. The last French troops withdrew in December 1946.
