Missionaries in 1671–75 founded outlying stations at Saint Ignace and Marquette. Jesuit missionaries were well received by the area’s Indian populations, with few difficulties or hostilities. In 1679, Robert Cavelier, Sieur de la Salle built Fort Miami at present-day St. Joseph. In 1691, the French established a trading post and Fort St. Joseph along the St. Joseph River at the present-day city of Niles.
18th century:
In 1701, French explorer and army officer Antoine de la Mothe Cadillac founded Fort Pontchartrain du Détroit or “Fort Pontchartrain on-the-Strait” on the strait, known as the Detroit River, between lakes Saint Clair and Erie. Cadillac had convinced King Louis XIV‘s chief minister, Louis Phélypeaux, Comte de Pontchartrain, that a permanent community there would strengthen French control over the upper Great Lakes and discourage British aspirations.
French attempts to consolidate the fur trade led to the Fox Wars involving the Meskwaki (Fox) and their allies versus the French and their Native allies.
At the same time, the French strengthened Fort Michilimackinac at the Straits of Mackinac to better control their lucrative fur-trading empire. By the mid-18th century, the French also occupied forts at present-day Niles and Sault Ste. Marie, though most of the rest of the region remained unsettled by Europeans. France offered free land to attract families to Detroit, which grew to 800 people in 1765, and was the largest city between Montreal and New Orleans. French settlers also established small farms south of the Detroit River opposite the fort, near a Jesuit mission and Huron village.
From 1660 until the end of French rule, Michigan was part of the Royal Province of New France. In 1760, Montreal fell to the British forces ending the French and Indian War (1754–1763). Under the 1763 Treaty of Paris, Michigan and the rest of New France east of the Mississippi River passed to Great Britain. After the Quebec Act was passed in 1774, Michigan became part of the British Province of Quebec.
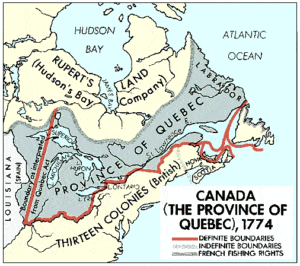
During the American Revolutionary War, Detroit was an important British supply center. Most of the inhabitants were French-Canadians or Native Americans, many of whom had been allied with the French because of long trading ties. Because of imprecise cartography and unclear language defining the boundaries in the 1783 Treaty of Paris, the British retained control of Detroit and Michigan after the American Revolution. When Quebec split into Lower and Upper Canada in 1791, Michigan was part of Kent County, Upper Canada.
Under terms negotiated in the 1794 Jay Treaty, Britain withdrew from Detroit and Michilimackinac in 1796. It retained control of territory east and south of the Detroit River, which are now included in Ontario, Canada. Questions remained over the boundary for many years, and the United States did not have uncontested control of the Upper Peninsula and Drummond Island until 1818 and 1847, respectively.
19th century:
During the War of 1812, the United States forces at Fort Detroit surrendered Michigan Territory, effectively consisting of Detroit and the surrounding area, after a nearly bloodless siege in 1812. A US attempt to retake Detroit resulted in a severe American defeat in the River Raisin Massacre. This battle, still ranked as the bloodiest ever fought in the state, had the highest number of American casualties of any battle in the war.
