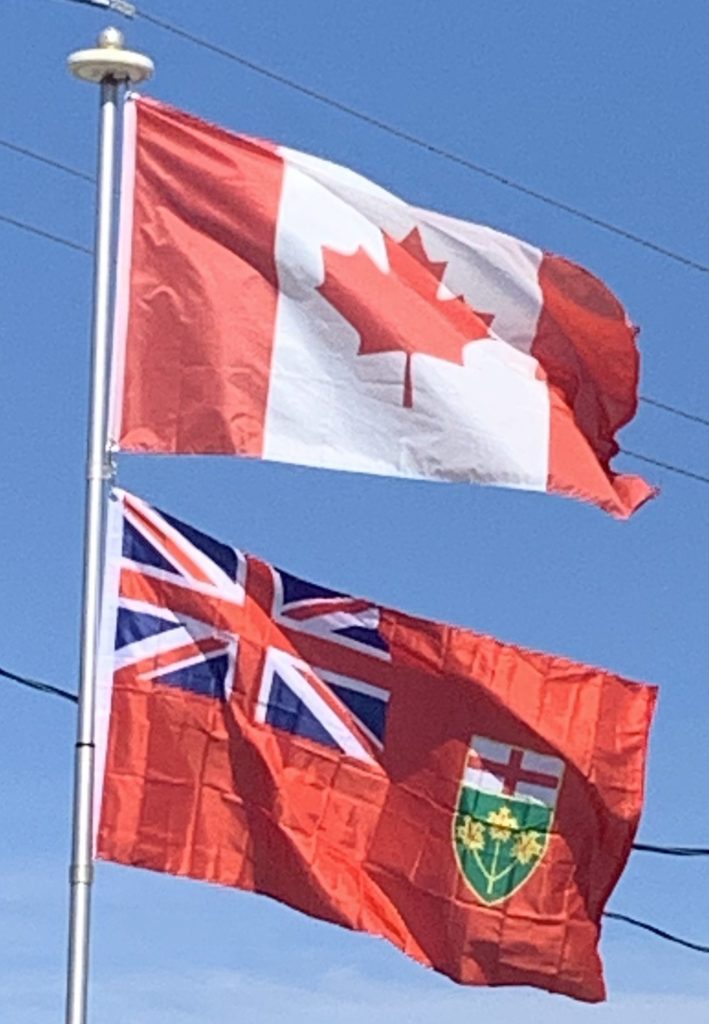
Introduction:
Ontario is one of the 13 provinces and territories of Canada. Located in Central Canada, it is Canada’s most populous province accounting for 38.3 percent of the country’s population, and is the second-largest province in total area. Ontario is fourth-largest jurisdiction in total area when the territories of the Northwest Territories and Nunavut are included. It is home to the nation’s capital city, Ottawa, and the nation’s most populous city, Toronto, which is also Ontario’s provincial capital.
Ontario is bordered by the province of Manitoba to the west, Hudson Bay and James Bay to the north, and Quebec to the east and northeast, and to the south by the U.S. states of Minnesota, Michigan, Ohio, Pennsylvania, and New York. Almost all of Ontario’s 1,678 mile border with the United States follows inland waterways: from the west at Lake of the Woods, eastward along the major rivers and lakes of the Great Lakes/Saint Lawrence River drainage system. These are the Rainy River, the Pigeon River, Lake Superior, the St. Marys River, Lake Huron, the St. Clair River, Lake St. Clair, the Detroit River, Lake Erie, the Niagara River, Lake Ontario and along the St. Lawrence River from Kingston, Ontario, to the Quebec boundary just east of Cornwall, Ontario. There is only about 0.6 miles of land border made up of portages including Height of Land Portage on the Minnesota border.
Ontario is sometimes conceptually divided into two regions, Northern Ontario and Southern Ontario. The great majority of Ontario’s population and arable land is in the south. In contrast, the larger, northern part of Ontario is sparsely populated with cold winters and heavy forestation.
Etymology:
The province is named after Lake Ontario, a term thought to be derived from Ontarí:io, a Huron (Wyandot) word meaning “great lake”, or possibly skanadario, which means “beautiful water” in the Iroquoian languages. Ontario has about 250,000 freshwater lakes.
Geography:
The thinly populated Canadian Shield in the northwestern and central portions, which comprises over half the land area of Ontario. Although this area mostly does not support agriculture, it is rich in minerals and partly covered by the Central and Midwestern Canadian Shield forests, studded with lakes and rivers. Northern Ontario is subdivided into two sub-regions: Northwestern Ontario and Northeastern Ontario.

Southern Ontario which is further sub-divided into four regions; Central Ontario (although not actually the province’s geographic center), Eastern Ontario, Golden Horseshoe and Southwestern Ontario (parts of which were formerly referred to as Western Ontario).
Despite the absence of any mountainous terrain in the province, there are large areas of uplands, particularly within the Canadian Shield which traverses the province from northwest to southeast and also above the Niagara Escarpment which crosses the south. The highest point is Ishpatina Ridge at 2,274 feet above sea level in Temagami, Northeastern Ontario. In the south, elevations of over 1,640 feet are surpassed near Collingwood, above the Blue Mountains in the Dundalk Highlands and in hilltops near the Madawaska River in Renfrew County.
